[ad_1]
Pests don’t plague petunias, however some acquainted backyard guests nibble foliage, stems, and buds and trigger weak spot. Detecting pests early is useful to forestall them from transmitting ailments, depleting crops of vitality, and impacting progress and flowering. Extreme infestations result in decline and unfold to different crops.
Many pests are most energetic in heat climate, the prime time for petunias’ showy show. Some thrive in humid, damp conditions, whereas others want sizzling and dry situations to proliferate. Vegetation pressured by environmental elements usually tend to succumb to pests and related ailments.
The greatest pest administration methodology is to supply petunias with their most popular rising situations. They want at the least 5 to 6 hours of daylight every day. Soils with constant moisture promote probably the most vigorous crops and prolific flowering. Fertilizer at planting and throughout the rising season helps the heavy feeders.
A biodiverse backyard with crops that entice helpful bugs and wildlife is a pure technique of pest management. Even with all the proper cultural situations, backyard pests occur. Right here, we’ll study widespread petunia pests and tips on how to determine, deal with, and stop them.
Spider Mites


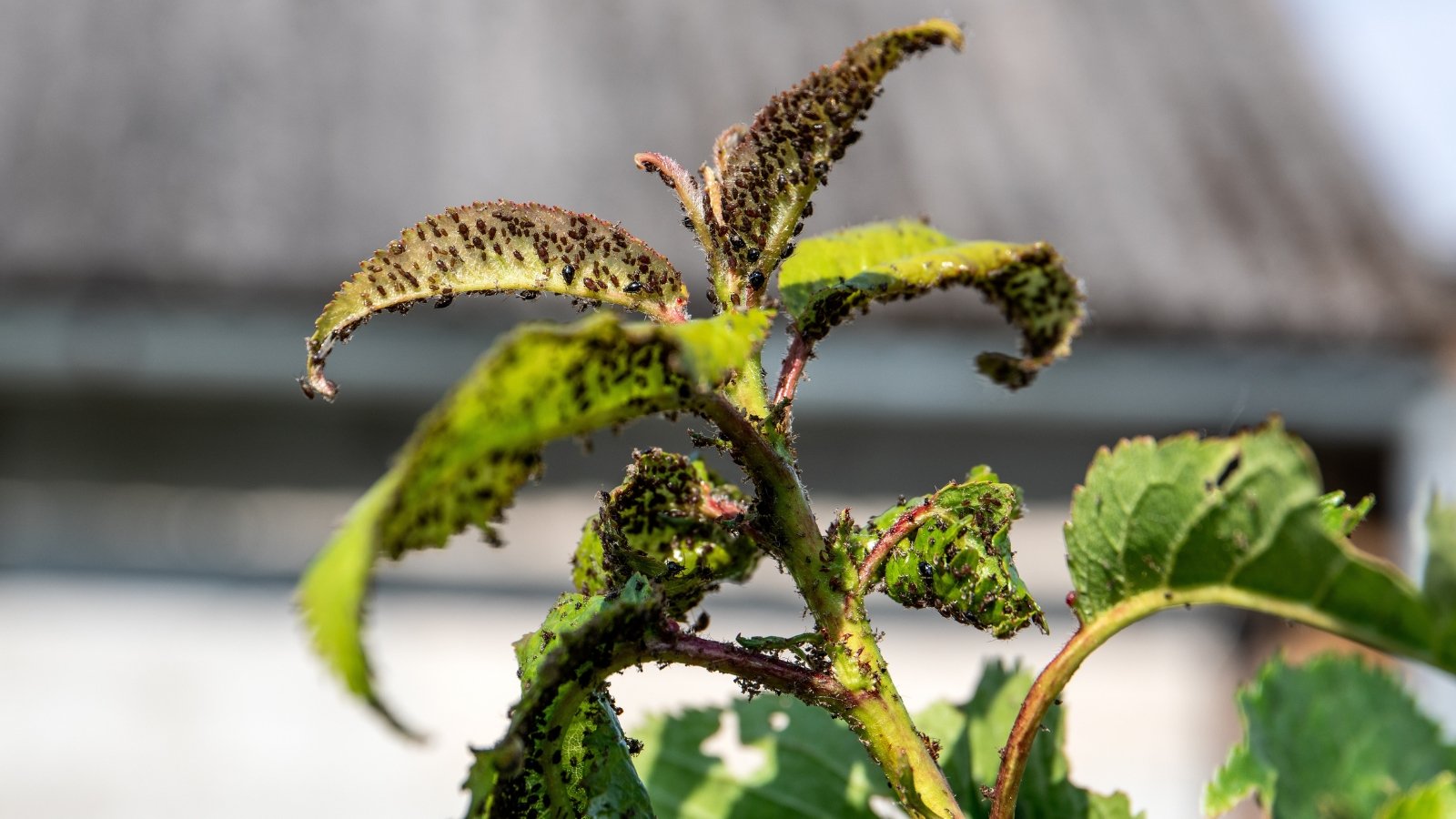
Spider mites are sap-sucking bugs that reside on the undersides of leaves. Their piercing mouthparts feed on mobile tissue. Chances are you’ll not see the tiny creatures and not using a magnifying glass, however their telltale webbing provides them away.
Colonies of the insect reside round leaf veins and mid-ribs beneath leaves. Females lay eggs, and the larvae shortly feed on sap and tissues. Pale spots seem on foliage. Adults feed and produce tight webs round leaves, stems, and branches.
The foliage reveals mild yellowing and stippling on leaf surfaces and will grow to be bronze. Leaves grow to be stiff and curl and will prematurely drop. Petunia flowers might discolor.
Spider mites happen in sizzling, dry, dusty situations. They flock to crops experiencing drought stress.
Therapy


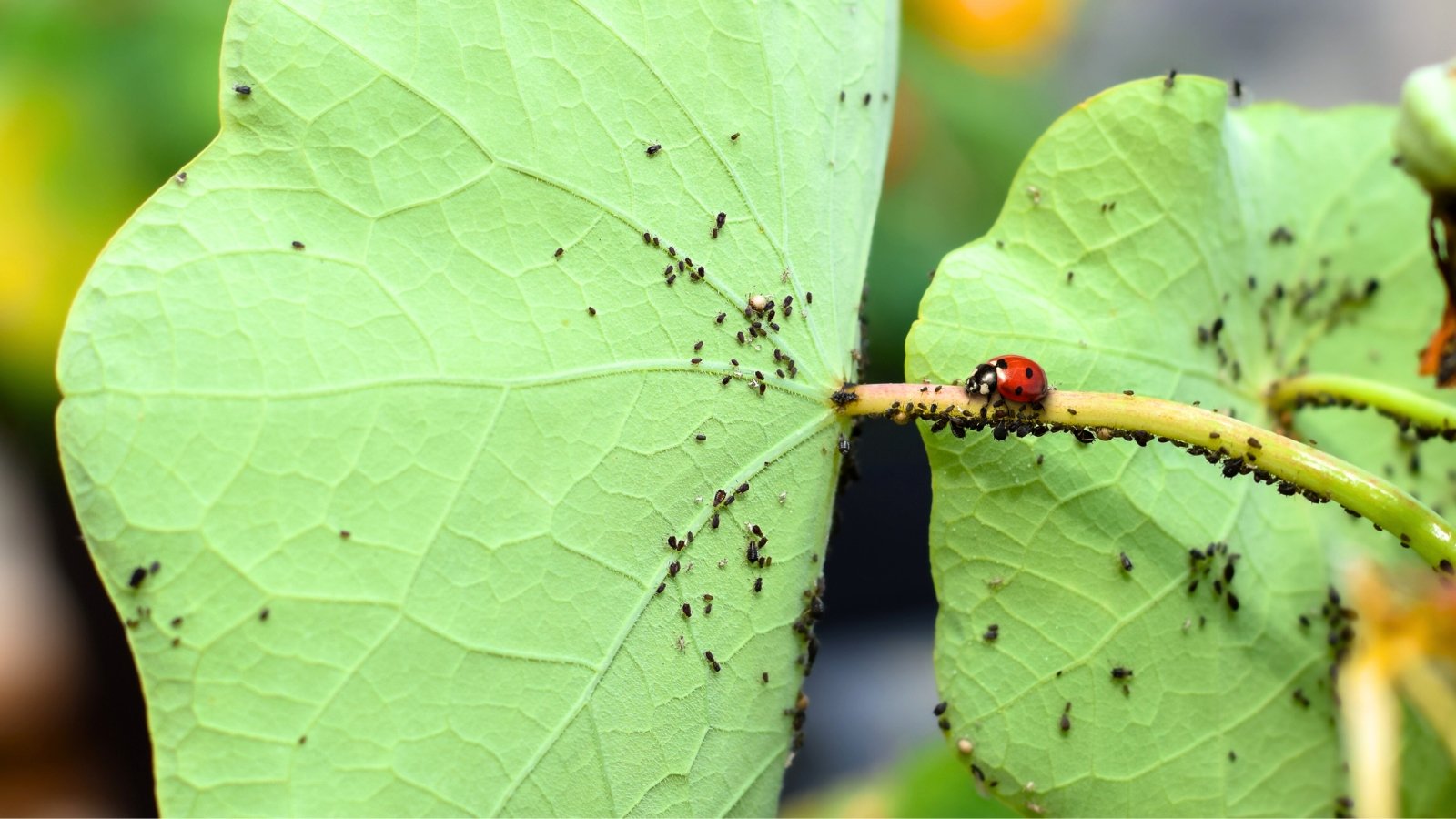
Helpful predatory bugs like ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites assist management populations. When you detect spider mites, spray the plant with a robust stream of water early within the day to discourage and knock bugs off the stems. Spraying additionally rinses mud off crops.
Prune away affected plant elements. Get rid of particles moderately than including it to the compost pile, which might harbor and unfold the bugs.
A easy horticultural cleaning soap or oil like neem rids the plant of extreme circumstances. Plant-based insecticidal oils like garlic extract, clove, rosemary, mint, and cinnamon oils are efficient natural controls. Remember to comply with label instructions, as these remedies have an effect on all bugs, together with pollinators. Time of day is crucial in utility, with earlier than or after sundown being the perfect.
To forestall spider mites, water petunias usually to keep up evenly moist soils. Whereas the annuals stand up to drying out between periods, greatest progress and flowering occur with constant moisture. Water fluctuations give spider mites an opportunity to extend, additional weakening crops.
Thrips
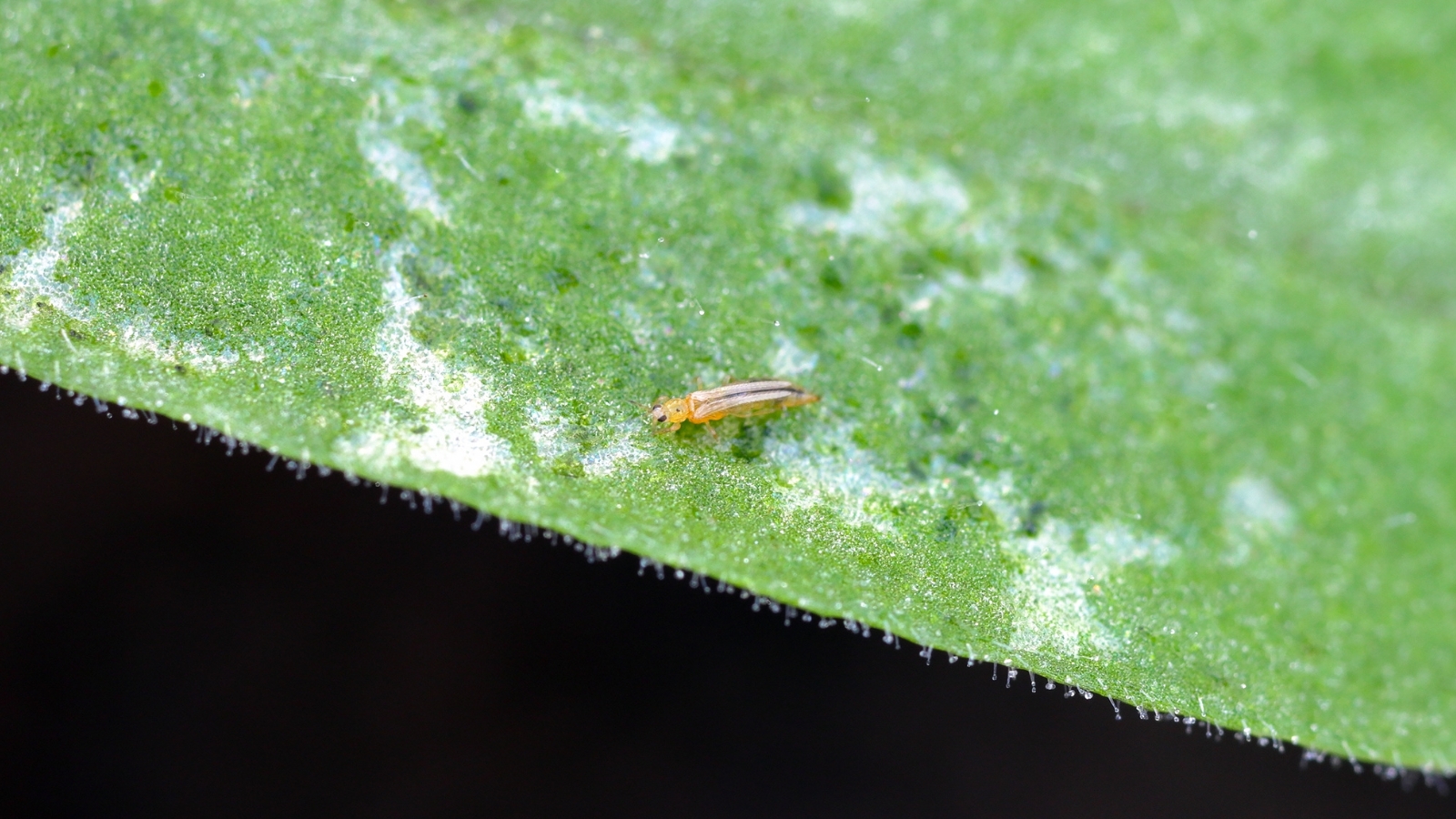


Thrips are a widespread pest. They’re tiny, slender bugs with lengthy, slim our bodies. Adults have fringed wings, and their coloration ranges from translucent white to yellow, brown, and black.
The bugs feed on flower and foliar tissues and carry viruses between crops. Western flower thrips are vectors of the impatiens necrotic spot virus and tomato noticed wilt virus, each of which impression and might kill petunias.
When thrips infest petal tissues, blooms develop white spots or distort. Leaves might seem silvery and stippled or brown and papery.
Not all thrips injury crops. Some feed on aphids and mites as pure pest management. When you see thrips however no indicators on the plant, maintain off on therapy. Therapy is so as if injury accompanies the insect otherwise you see injury alone. It’s simple to regulate thrips early on and with common scouting.
Therapy
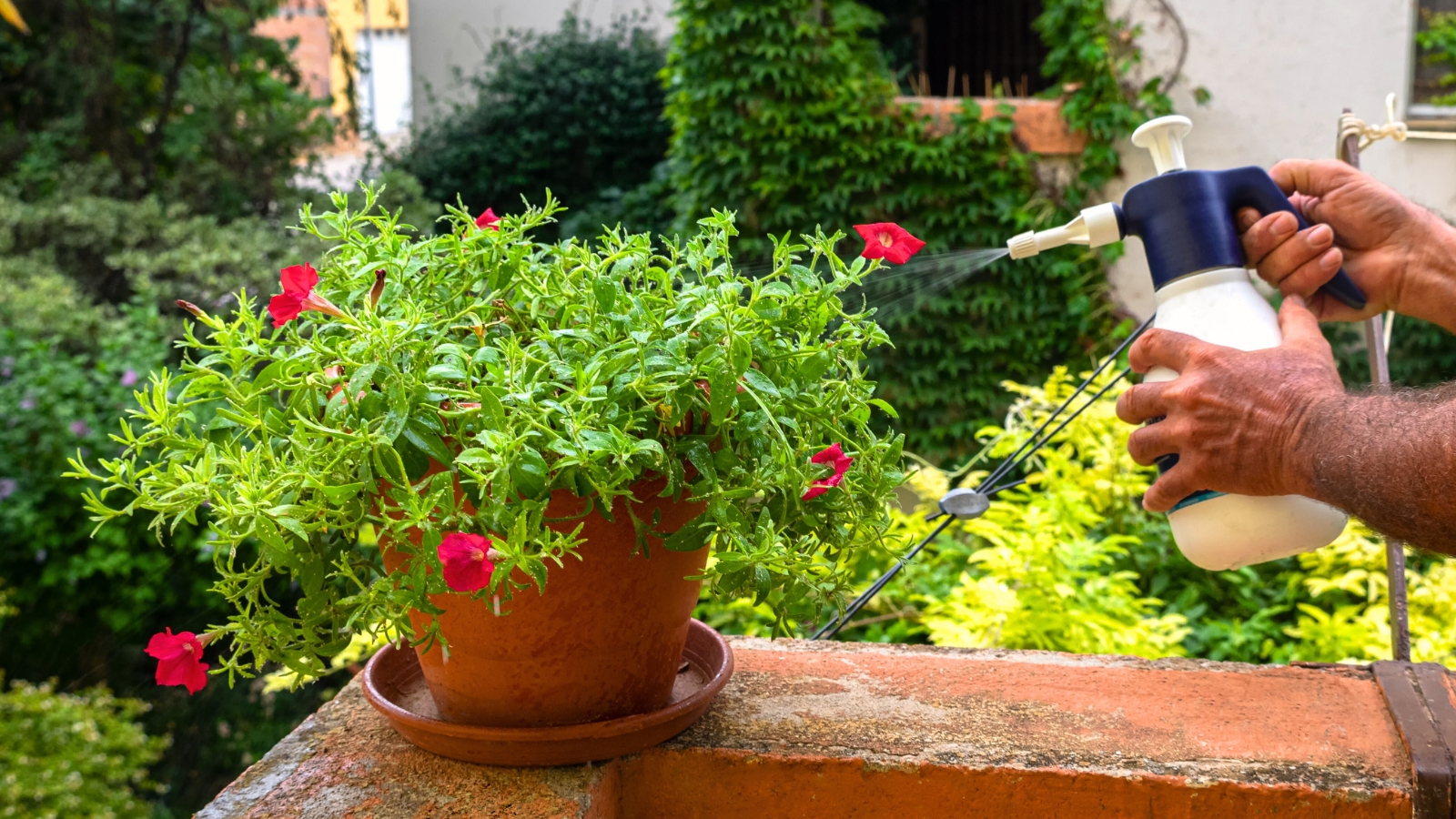


As with spider mites, helpful predatory bugs like parasitic wasps, different mites, and inexperienced lacewings naturally management thrips. Rinse the mud off crops to advertise beneficials and deter plant-feeding bugs. Minimize off and discard affected plant sections.
Neem oil or horticultural soaps deal with infestations. Spinosad, derived from a micro organism, organically treats thrips by disrupting their feeding course of and killing the insect. Keep away from making use of it when pollinators are current, as it’s extremely poisonous to bees till it dries.
Budworms
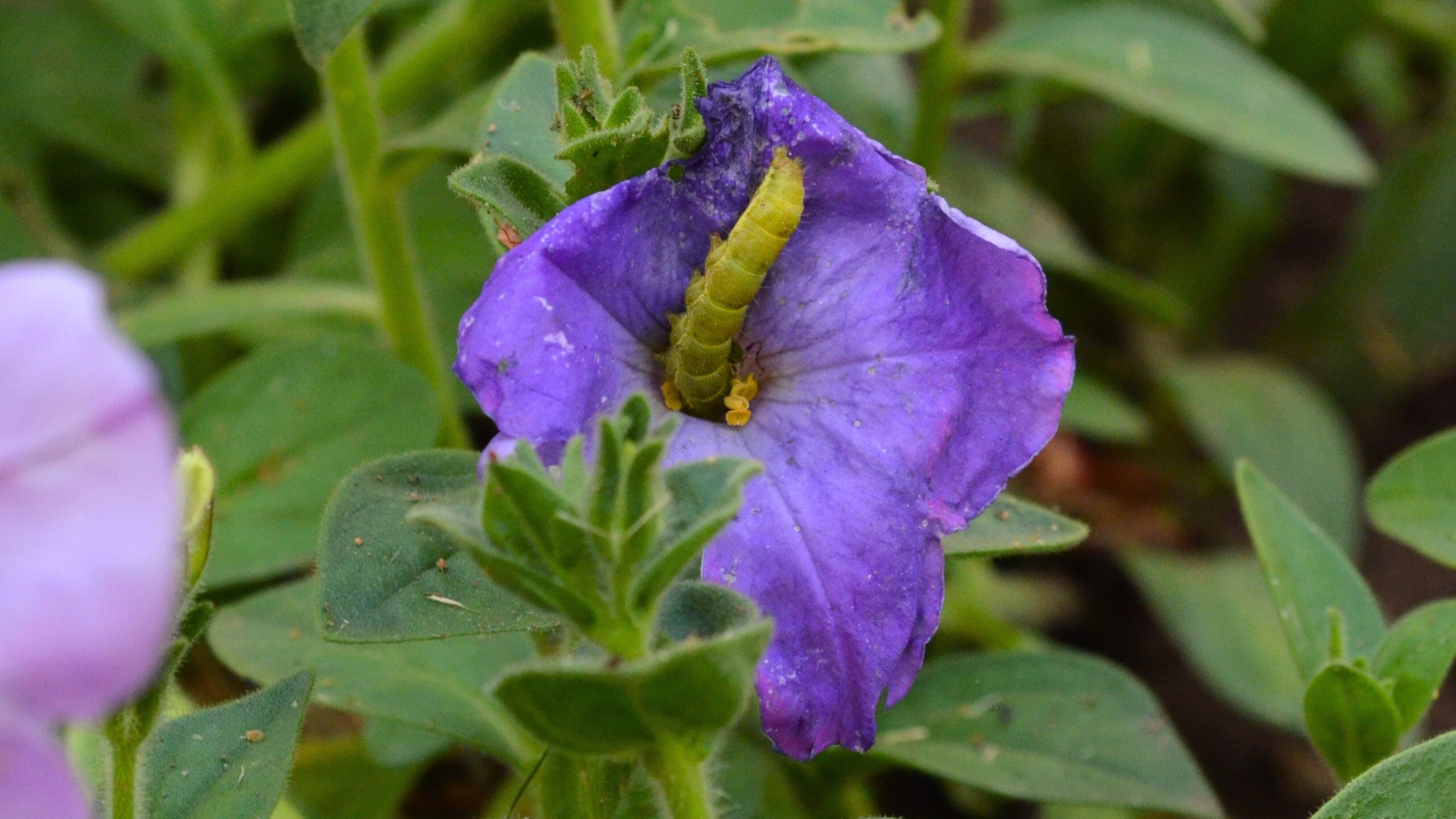


Budworms are caterpillars that feed on stems, leaves, and buds. Their voracious appetites trigger fast injury. To preserve your petunias blooming all season, preserve a watch out for caterpillars.
The tobacco budworm feeds on petunia buds and petals. It’s most energetic at night time, and affected blooms might not open throughout the day. Chances are you’ll discover chewed petals and budworm droppings.
The grownup is a grey moth who lays eggs on the undersides of leaves. The caterpillars hatch inexperienced or mild rust-colored. Small holes in leaves and petals point out early infestation.
The quantity grows over the seasons in areas the place host crops are repeatedly grown. The inhabitants grows as extra budworms hatch, feed, and pupate within the surrounding soil to grow to be grownup moths.
Therapy

Thankfully, each the caterpillars and their injury are simple to identify. You possibly can hand-pick them off crops within the morning or night after they’re most energetic. Within the warmth of the day, you’ll discover them resting on the soil stage close to the bottom of the plant. Bacillus thuringiensis (BT) is a micro organism that disrupts digestion and causes the budworms to cease feeding. It’s a organic management.
If budworms are an issue, rotate petunia rising areas yearly. Petunias are a part of the Solanaceae (nightshade) household, together with tomatoes, peppers, tobacco, flowering tobacco, eggplants, and plenty of different decorative and meals crops. Pests and ailments simply switch between nightshade members. Rotating crops or offering distance between choices helps reduce the transmission.
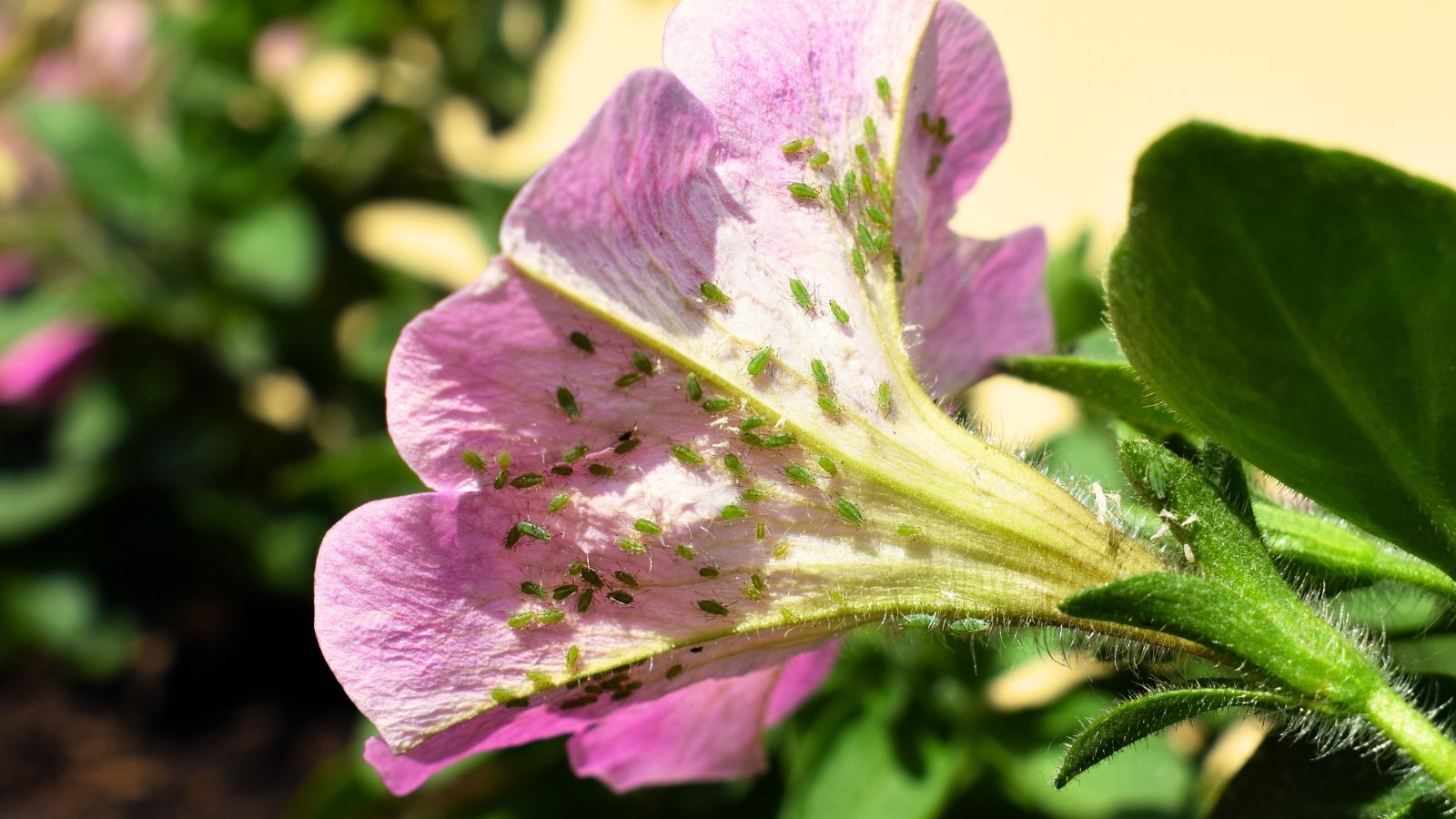
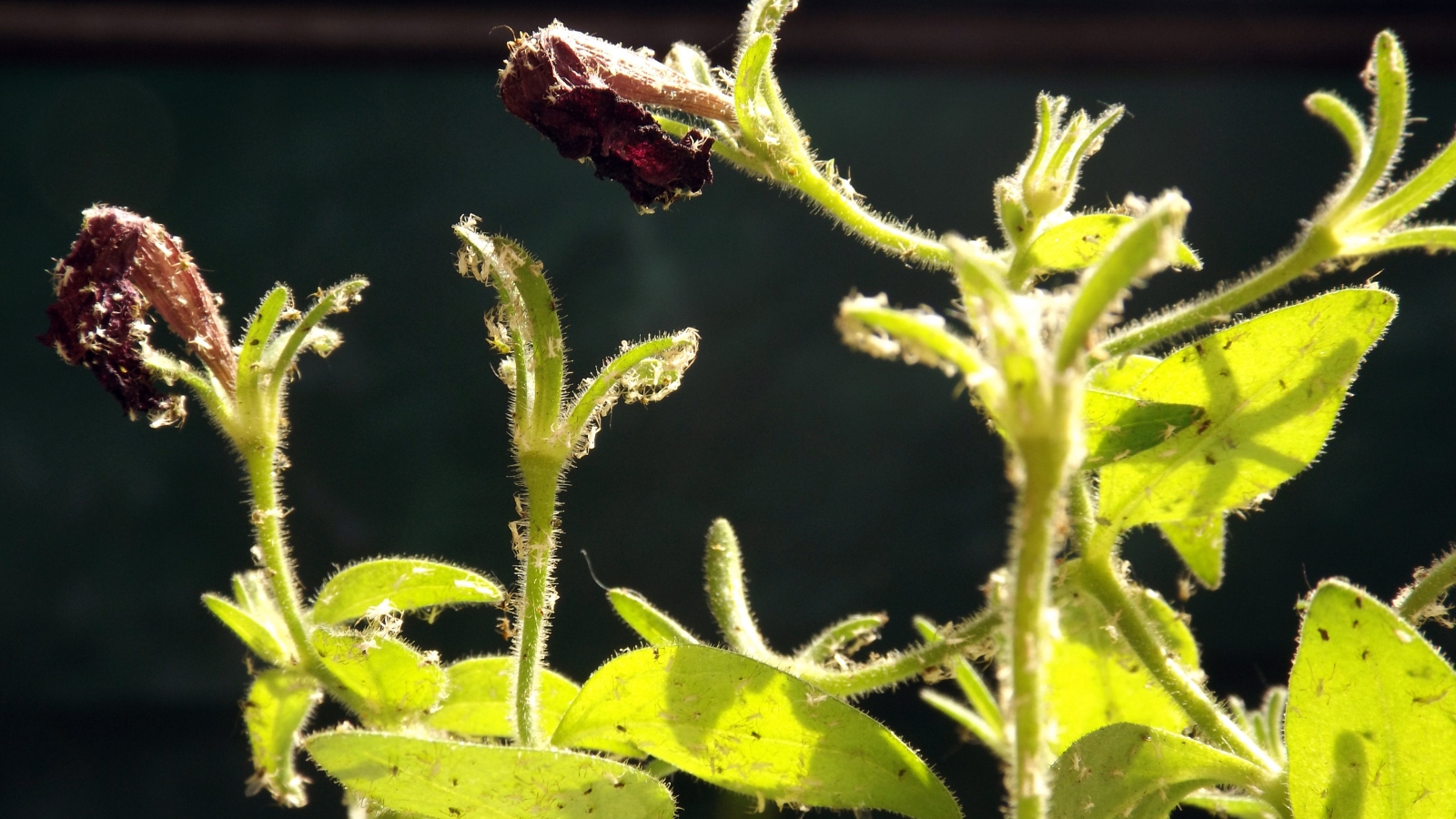
Aphids
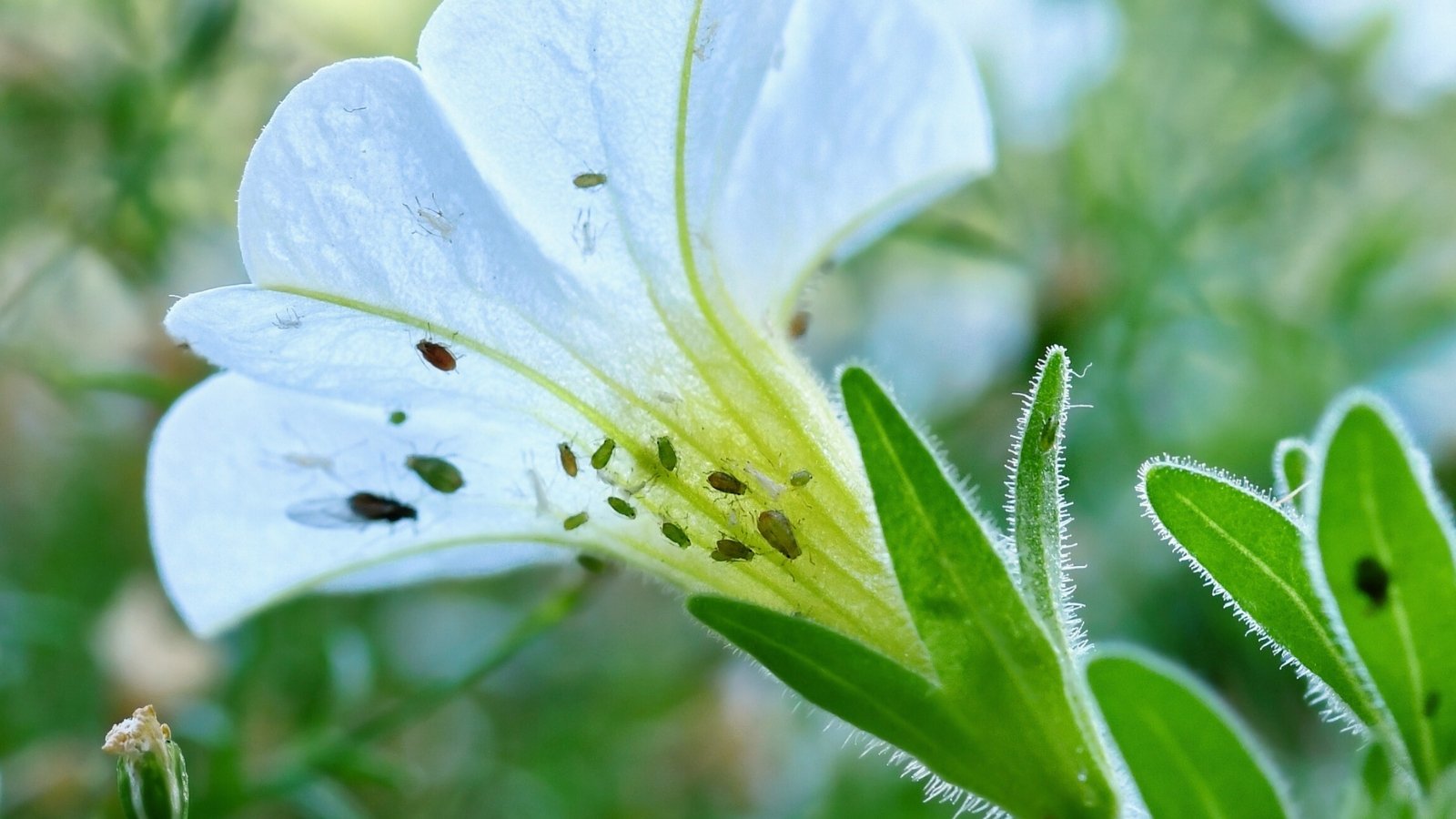


Aphids are all-too-common sap-sucking bugs that feed on quite a lot of crops. They don’t typically pose a extreme risk however can stress crops and depart behind sticky honeydew, resulting in black, sooty mildew. Aphids unfold fungal spores and are vectors for viruses, together with mosaic viruses, that are lethal in petunias.
Aphids are pear-shaped, soft-bodied, and light-weight yellow, inexperienced, pink, brown, or black. They collect in massive numbers on the undersides of leaves.
Vegetation with extreme infestation might expertise curled leaves, yellowing, and stunted progress. Chances are you’ll discover virus or fungal illness signs like leaf spots, mottling, and distortion.
Therapy


As with spider mites and thrips, spraying the plant with a robust stream of water early within the day might deter them by knocking them off leaves and stems. The stream separates the mouthparts of piercing bugs from their our bodies. Do that usually as a part of ongoing upkeep.
Since aphids congregate in numbers, pruning off impacted sections could also be sufficient to management small infestations. Horticultural cleaning soap or oil controls infestations. Dusting crops and soil with diatomaceous earth might stop the unfold. The powder creates a pointy floor that damages soft-bodied bugs.
To forestall aphids, make use of constant watering for evenly moist soils. They’ll gravitate towards drought-stressed petunias over wholesome, well-watered specimens. Embody a variety of crops to draw predatory bugs.
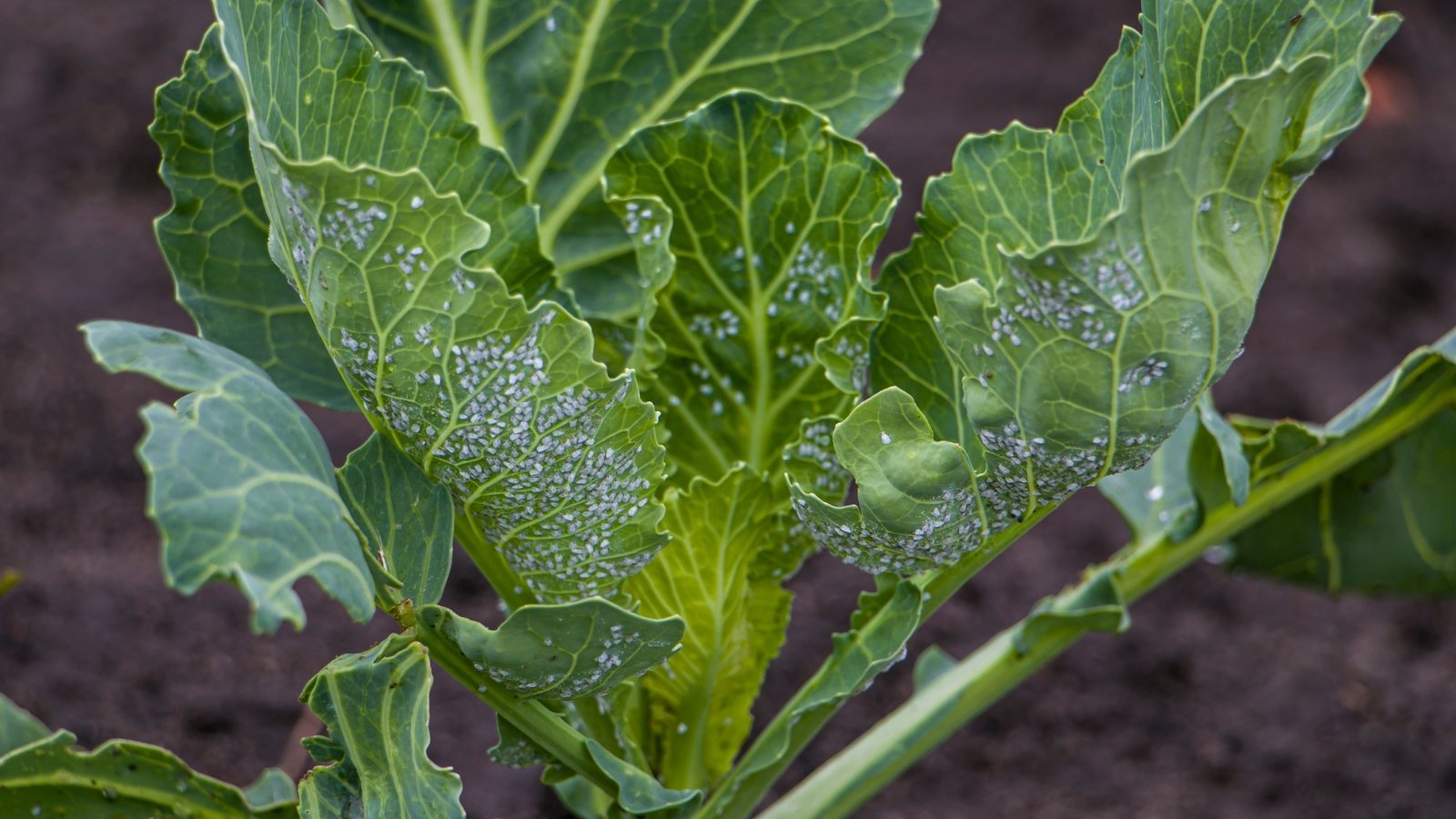
Leaf Miners
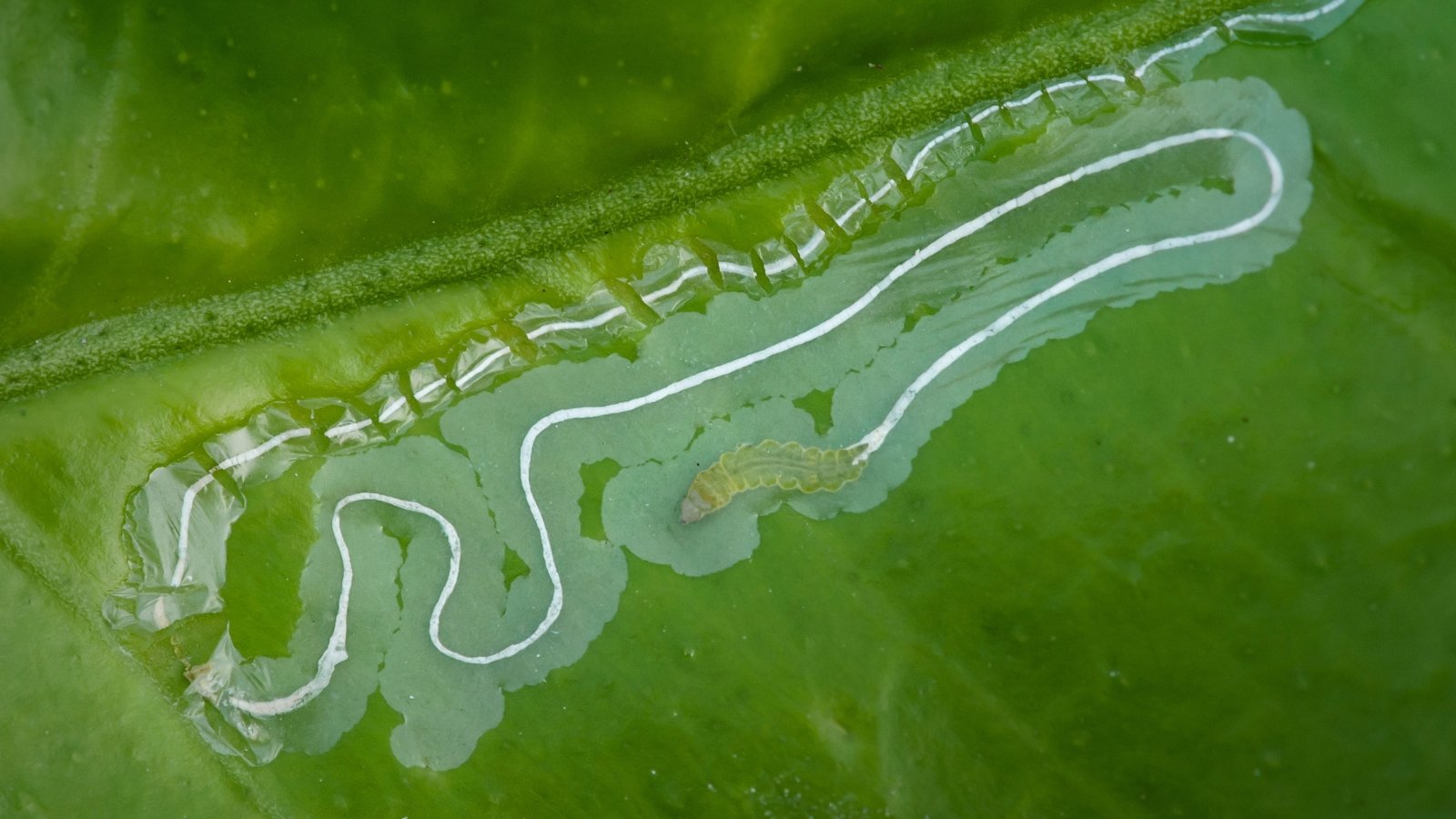


Leaf miners (fly larvae) burrow and tunnel into leaves. The larvae are yellow, cylindrical, and seedlike. Grownup leaf miners are small black flies. They typically have a yellow triangle on the base of their wings.
Leaf miners depart paths and punctures that deform foliage and petals. Plant elements grow to be yellow and blotchy. The larvae feed beneath the leaf floor, leaving winding trails.
Grownup leaf miners pierce leaves and petals to entry sap and lay eggs. The punctures flip white for a speckled look.
Thankfully, leaf miners not often severely injury crops. Heavy injury can sluggish plant progress and trigger leaves to drop, and their mining might create openings for fungal an infection.
Therapy


Helpful bugs like lacewings and predatory wasps prey on leafminers. Eradicating broken leaves simply defrays a light-weight infestation.
Crush trails to squelch the miner. Neem oil, BT, and spinozad sprays management infestations.
To forestall leaf miners, consider irrigating for constant moisture. Keep away from overwatering and extended intervals of moisture. Irrigation monitoring isn’t a lot for the leaf miner however for related fungal infections like root rot that simply unfold from soil to plant by way of the insect.
Slugs and Snails
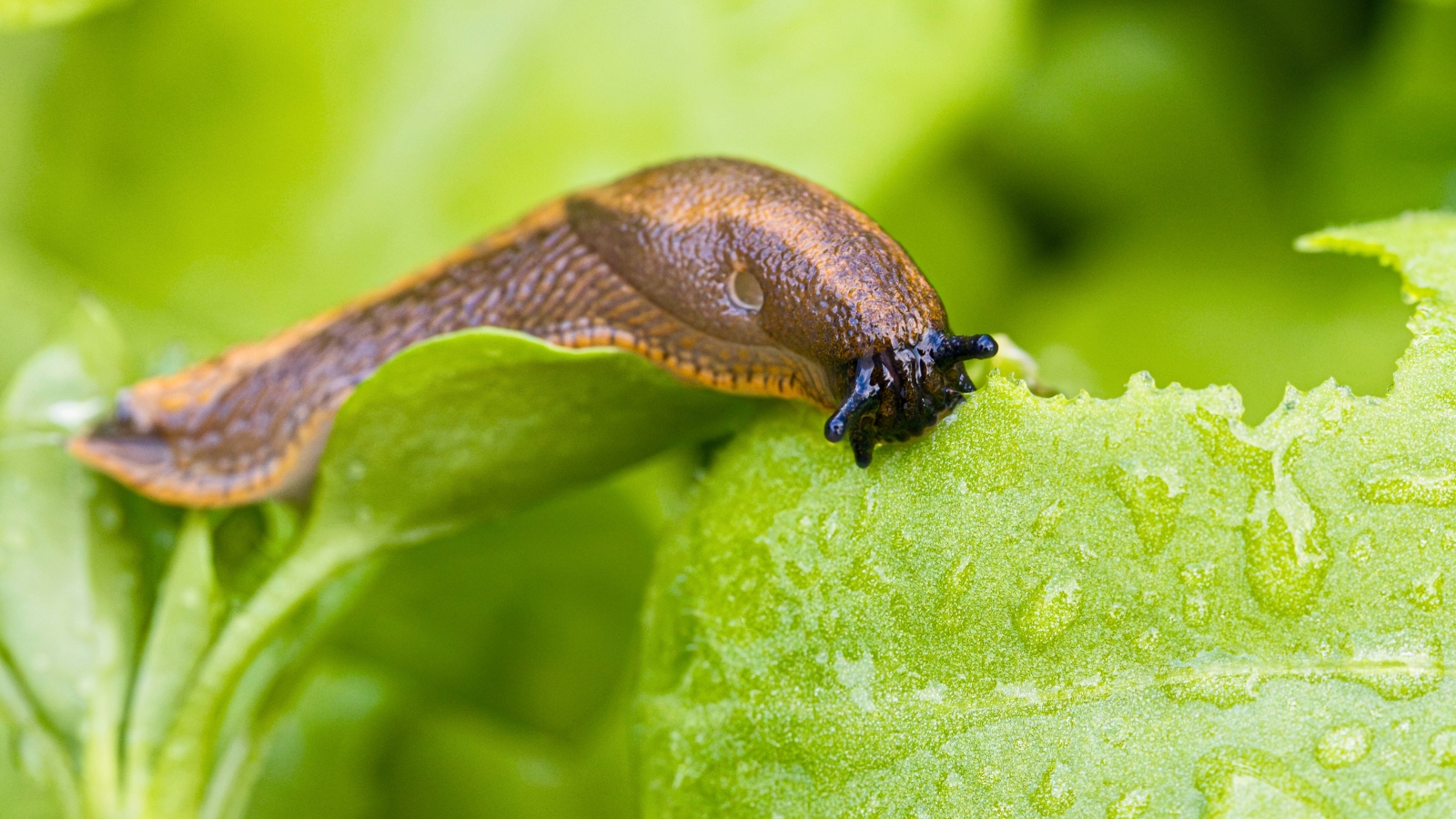


Slugs and snails might graze on crops, particularly contemporary shoots and gentle progress. They could solely do minor injury. Snails and slugs are meals for wildlife like birds and frogs.
When you see the creatures and spot nibble injury, a treatment could also be so as. Thankfully, snails and slugs are simple to see of their most energetic instances of day.
Therapy
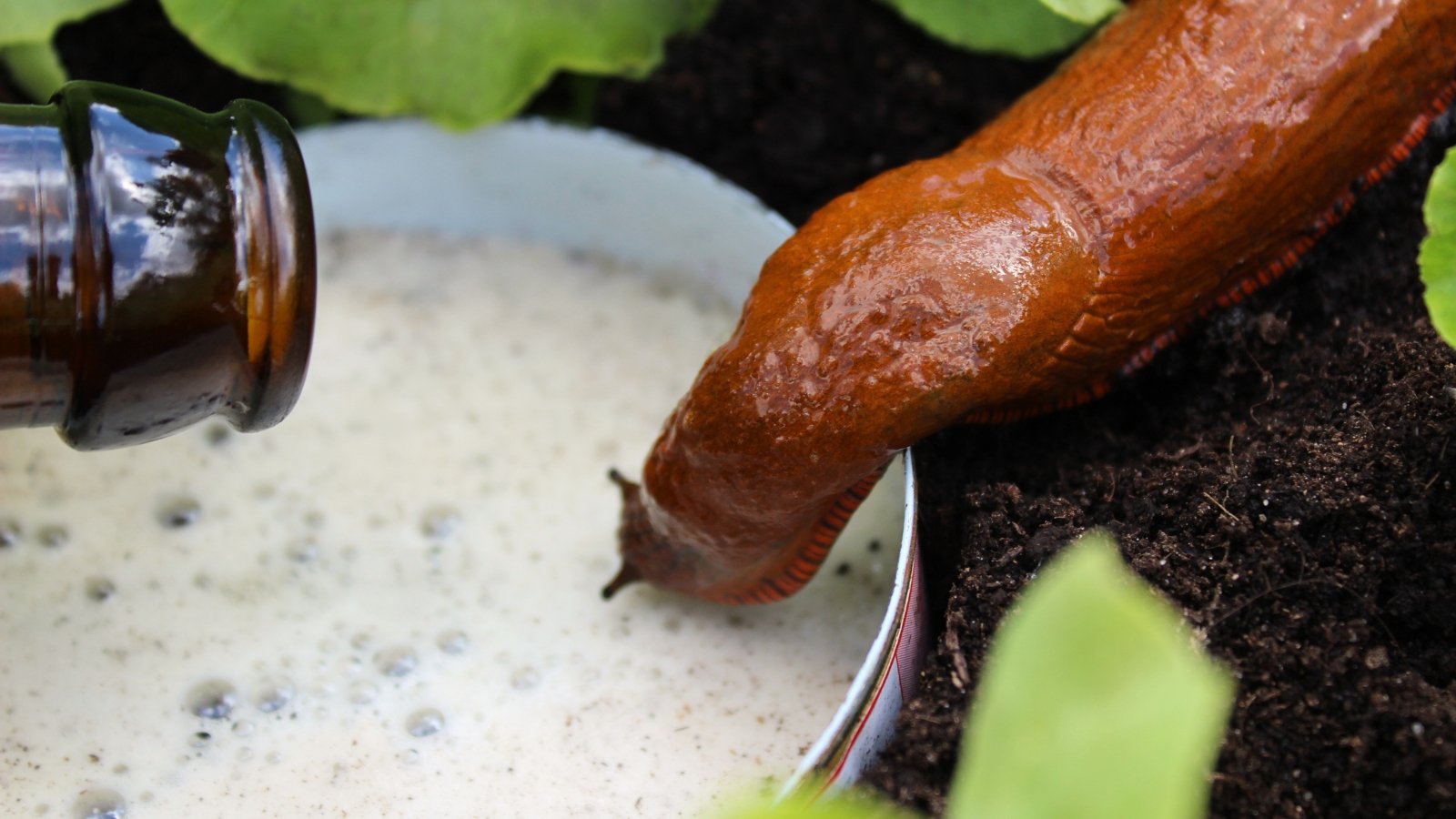


Hand-pick them early within the day or night after they’re most energetic. In the midst of the day, they’ll tuck in underneath leaves or on the soil across the base of the crops. If numbers enhance, bait them with beer or soda traps by filling a shallow dish and inserting it at soil stage.
Flea Beetles
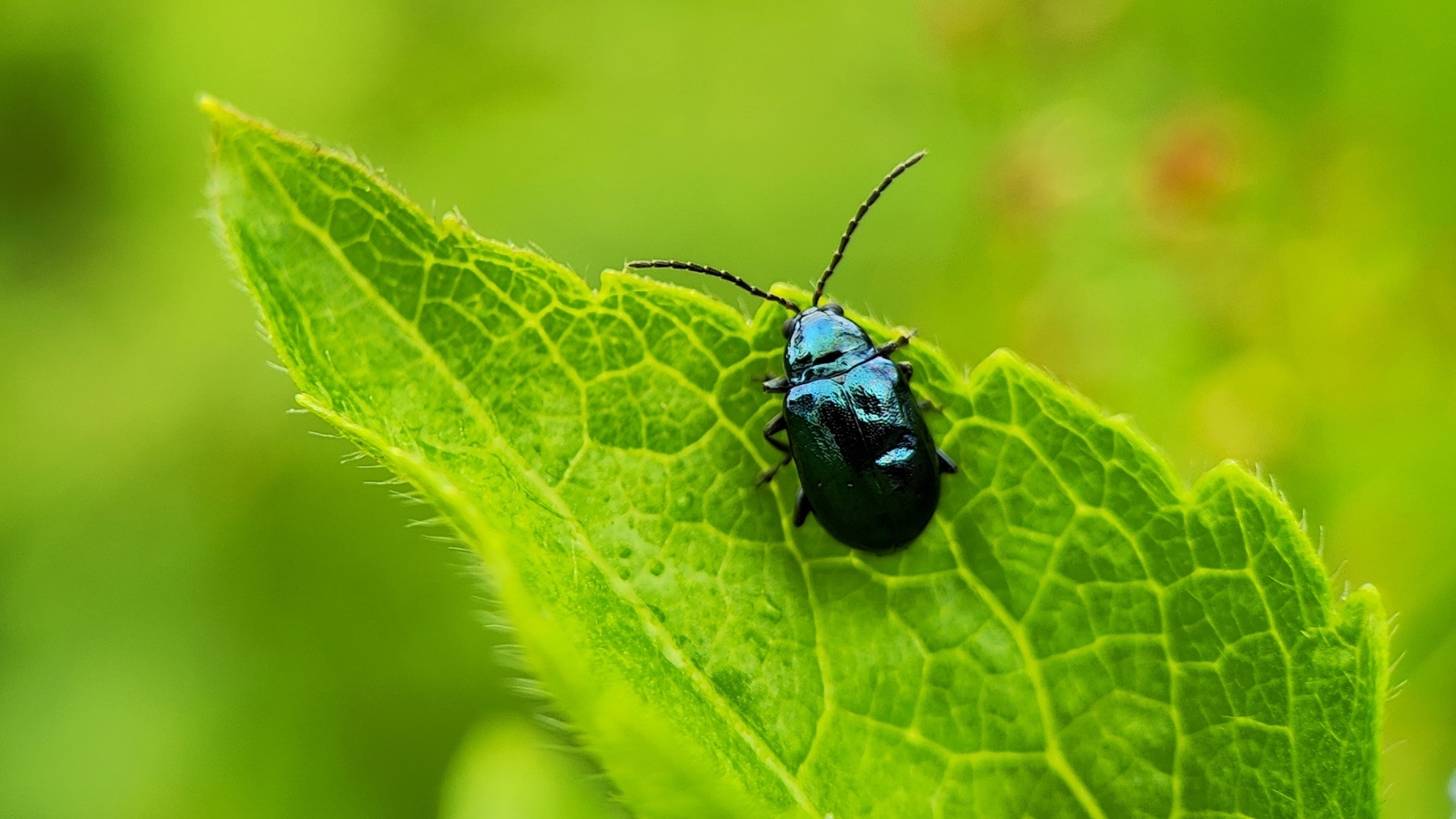


Flea beetles aren’t fleas however small bugs that hop from leaf to leaf, shortly skeletonizing foliage as they go. They’re most energetic within the spring. Flea beetles are widespread and have many species. A number of, together with potato and tobacco flea beetles, are susceptible to petunias.
Potato flea beetles are shiny black, whereas tobacco fleas are brown with massive, darkish spots on each side of their our bodies. These are widespread in hotter areas and like nightshades.
Grownup flea beetles feed on plant materials. They lay eggs beneath the soil floor, the place larvae hatch to feed on tender roots. The larvae grow to be grownup beetles to feed on the plant. Leaf surfaces grow to be mottled yellow and brown and will skeletonize, with solely the veins remaining.
Therapy
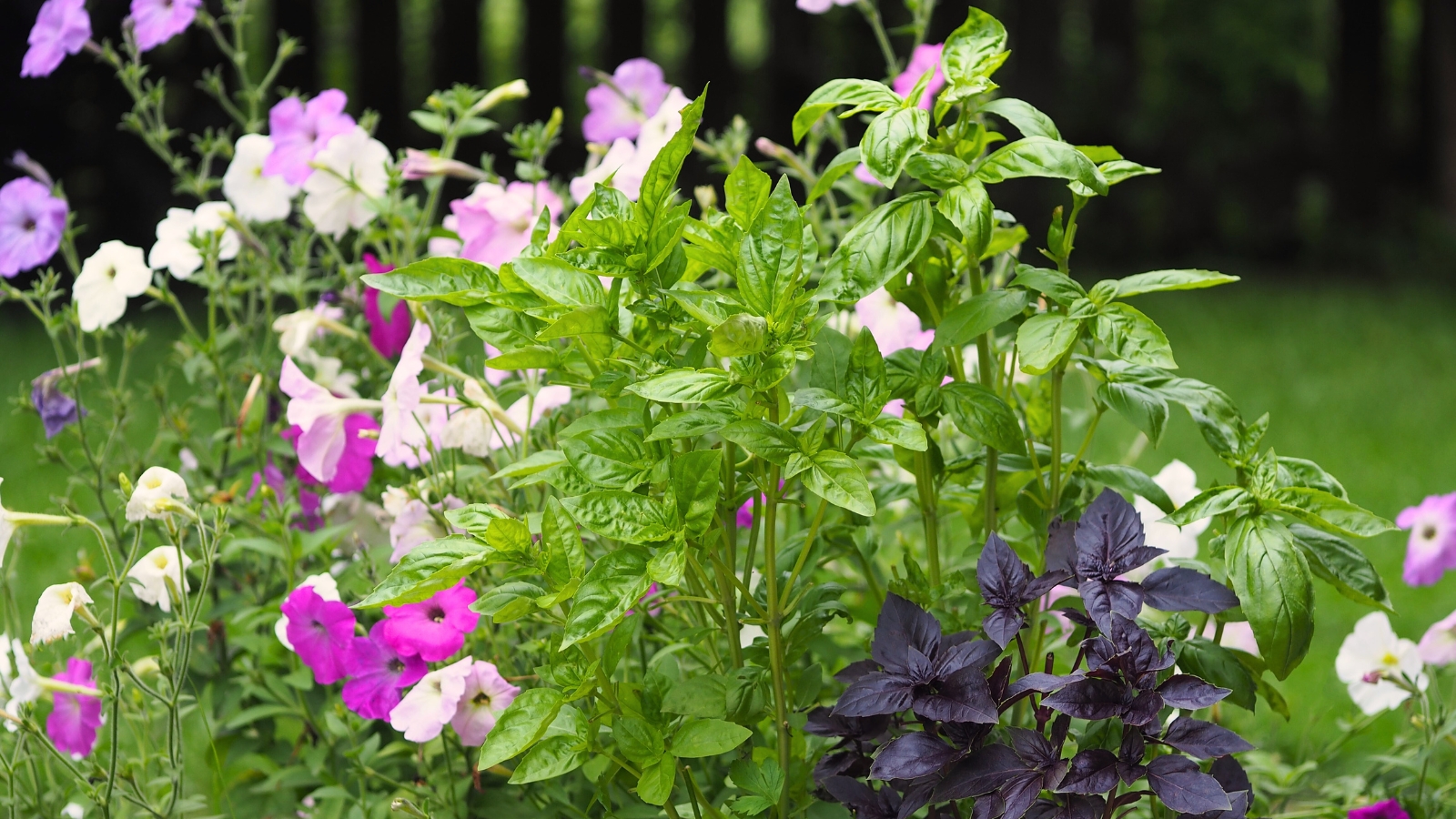


Interplant with crops to repel bugs, corresponding to catmints, basil, and marigolds. Natural remedies embrace spinosad or pyrethrin sprays and horticultural oils like neem. Diatomaceous earth utilized to the plant surfaces helps management outbreaks.
[ad_2]










